
Customer relationship management and email marketing operate are more deeply interconnected than you may expect. When these systems work in isolation, businesses miss critical opportunities to engage customers meaningfully.
Proper alignment between CRM and email marketing transforms how organizations nurture relationships, manage data, and execute campaigns.
Here’s Nutshell’s guide to creating that alignment through strategic people, process, and data governance planning.
Most organizations view their CRM system and email marketing platform as separate operational functions. Sales teams use the CRM to manage relationships and track interactions, while marketing teams execute campaigns through their email platform. This compartmentalization creates real business costs.
According to recent research, 45% of companies cite automation as their top CRM priority, followed closely by integration at 36%. The fact that more than one in three companies identifies integration as a critical need signals widespread recognition of the problem.
When customer data lives in disconnected systems, teams face several challenges:
These gaps don’t just create inefficiency—they directly impact revenue. When your team can’t see the complete customer picture, email campaigns lack relevance, sales follow-ups miss important context, and customers experience disjointed interactions instead of cohesive journeys.
That’s why it’s so vital to integrate your CRM with email marketing campaigns. Of course, there are steps you need to take to set your strategy up for success first.
Effective alignment requires attention to three distinct but interconnected areas: the people who manage these systems, the processes that govern their interaction, and the data structures that support them.
Sales and marketing teams must establish shared understanding and communication patterns. This means:
Without people alignment, even technically perfect systems fail. Teams need to understand not just what data goes where, but why those decisions matter for customer experience.
Your workflows should connect logically across both systems. Practical examples include:
Process alignment prevents gaps where information exists but doesn’t flow to the people who need it. A customer service team might resolve an issue that marketing was unaware of, leaving marketing to send irrelevant offers days later. Proper process design ensures that interaction occurs in both systems, creating institutional memory.
This is the organizational framework that determines how customer data moves between systems. Core elements include:
According to best practices documentation on data synchronization, organizations that implement formal data governance see significant improvements in data quality metrics and report substantially fewer duplicate records. Data governance often feels like an administrative burden, but it’s the foundation that makes alignment actually work.
Customer data sits at the heart of both CRM and email marketing operations. When managed well, this data enables personalization and efficiency. When managed poorly, it becomes a liability. The fundamental requirement is establishing a single source of truth for customer information.
This doesn’t necessarily mean that all data lives in one platform, but rather that a clear hierarchy exists, specifying which system owns which data elements. Many organizations designate the CRM as the primary record for contact information, while treating the email platform as a specialized tool that receives curated data.
Real-time data synchronization between systems is the ideal state, although it’s not always technically feasible. At minimum, establish regular sync cadences—perhaps daily for active contacts and weekly for less engaged prospects.
Research on data synchronization best practices emphasizes that synchronization lag time should be monitored continuously, with most systems aiming to keep lag times within a few seconds to minutes for mission-critical data flows.
Approaches that support data consistency include:
Customer data also needs regular hygiene maintenance. This means removing duplicates, correcting incomplete records, and removing opt-outs across both systems. Many teams discover that their first alignment project reveals data quality issues that have accumulated over months or years. Plan time and resources for this cleanup—it’s an investment in long-term accuracy and reliability.
Email marketing combined with CRM data enables automation that delivers messages at precisely the right moments. Rather than sending the same message to everyone on a list, you can create sequences that respond to specific actions.
Automated emails achieve roughly 70% higher open rates than non-automated messages, and top-performing email workflows generate $16.96 per recipient compared to $1.94 for standard email flows. This dramatic difference isn’t coincidental—it reflects the power of relevance and timing.
Effective workflows typically rely on triggers from CRM data. Common examples include:
For these workflows to function properly, your CRM and email system need to share field definitions. If your CRM designates a contact’s status as “Marketing Qualified Lead” but your email platform refers to it as “MQL,” create explicit mapping so that status changes in one system are automatically reflected in the other.
Research on trigger-based marketing reveals that behavioral triggers—such as cart abandonment or product page visits—combined with precise timing and relevant messaging, achieve significantly higher open rates and engagement levels than static email campaigns. The key is to ensure that your CRM captures the behavioral data that email systems need to accurately fire these triggers.
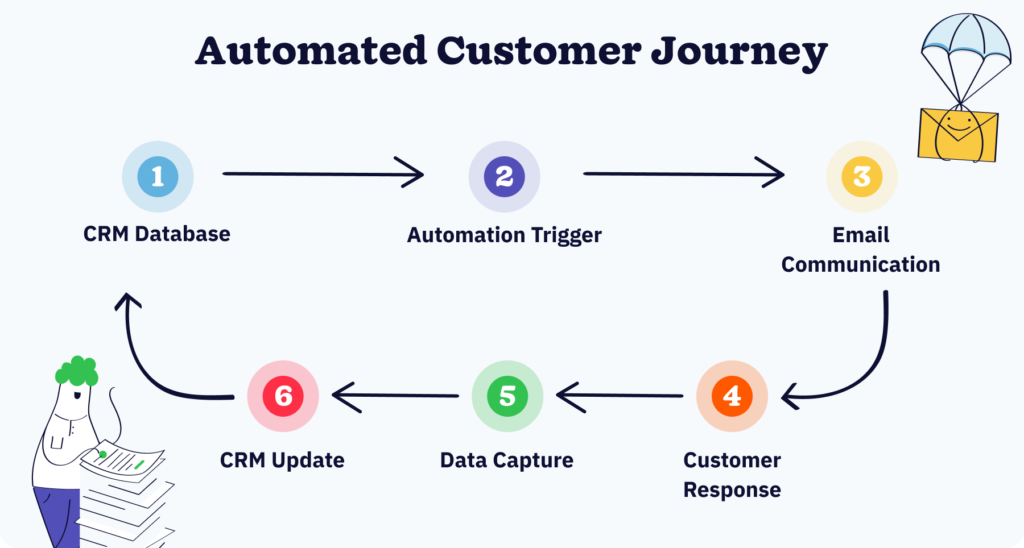
Once CRM data is structured and enriched, organizations can activate it through a variety of automated workflows. This involves using intent signals, behavioral triggers, and enriched firmographic data to determine the right moment and message for outreach. For example, a CRM entry enriched with recent funding data or hiring signals might trigger a sales development sequence, while low-engagement activity could prompt a reactivation email flow.
Specialized GTM partners help organizations build this layer of intelligence by combining enrichment tools with routing logic and workflow design. These systems can power ABM programs, personalized messaging, or BDR outreach tracks—based entirely on real-time CRM inputs. By using the CRM not just as a repository but as an activation engine, teams unlock more precise, relevant, and timely communication across both marketing and sales.
Despite the clear benefits, CRM and email marketing integration encounter real obstacles. Most of these challenges have solutions, but they require planning rather than hoping integration will “just work.”
The most frequent problem occurs when integration was never implemented or failed after being partially deployed. Data flows in one direction, but not the other, or updates to one system don’t reflect in the other.
The solution requires either implementing proper two-way synchronization or accepting the limitations and training teams to manually sync critical data points. Some organizations use platform-agnostic tools, such as Zapier, to bridge systems that lack native integrations.
Even with integration, a delay may exist between when data changes in one system and when it is reflected in another. For time-sensitive campaigns (like abandoned cart reminders), these delays matter significantly. Evaluate whether your integration architecture supports the speed your business requires.
Email reputation deteriorates when poor data management causes duplicate sends, invalid addresses, or excessive unsubscribes. Ensure your CRM-to-email sync includes validation that removes suppressed addresses and invalid email formats before sending.
When systems use different field names or field types for the same information, mapping errors occur. Invest time in documenting exactly which CRM fields map to which email platform fields, and audit these mappings quarterly as systems are updated.
Some team members need to view all customer data, while others should only see specific segments. Misaligned permission structures can either expose sensitive data inappropriately or leave team members unable to perform their jobs effectively.
How do you know if your CRM and email alignment efforts are working? Several metrics provide clarity.
Most importantly, establish feedback loops that allow team members to report when the system isn’t meeting their needs. Conduct regular check-ins with sales representatives and marketing specialists to identify friction points that metrics may miss. Then, prioritize fixes based on their impact on work.
Most organizations complete alignment within 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the system. Initial setup (4 to 6 weeks) covers auditing data, identifying integration requirements, and mapping fields. Testing and training take 2 to 4 weeks. Going live and optimization takes another 2 to 4 weeks. Remember that alignment is an ongoing process—plan quarterly reviews and annual audits as your business evolves.
One-way sync pushes data from CRM to email (or vice versa), but doesn’t bring it back. This is simpler but creates incomplete records. Two-way sync enables data to flow in both directions—email engagement is returned to the CRM, and CRM activities are reflected in email histories. Two-way requires more careful data governance but delivers far better results and eliminates the need for manual data entry.
Small teams (under 50 people) can manage alignment as part of existing marketing or sales operations roles. Medium-sized teams (50 to 500 people) typically benefit from having one person dedicate 10 to 20 hours weekly to maintenance and monitoring. Larger enterprises may need a dedicated specialist. Start by assigning responsibility to an existing team member and reassess if the workload consistently exceeds 10 hours per week.
Middleware platforms like Zapier, Make, or PieSync can connect most systems affordably (ranging from $20 to $100/month) without requiring custom coding. These handle standard needs, such as syncing contacts and logging activities. Only pursue custom API integration if the middleware doesn’t meet requirements after 2 to 3 months of testing. Avoid overcomplicating integration until you know exactly what you need.
Understand your compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR and CCPA) before integrating with the platform to ensure seamless integration. Ensure that unsubscribes sync across systems and deletions occur simultaneously on all platforms. Document your data flow, implement role-based access controls, and conduct a privacy impact assessment before implementation. Then, review the process annually. Proper governance actually enhances your privacy posture by providing visibility into where customer data resides.
Aligning CRM and email marketing requires a coordinated effort across three key areas: establishing people alignment so that teams understand how to work together, designing processes that move information where it needs to go, and implementing data governance to ensure quality and consistency.
The business case is clear. When these three components work together, customers experience more timely and relevant communication. Sales teams have complete visibility into customer interactions. Marketing teams can target with greater precision. And organizations gain the efficiency advantage that comes from automation and reduced manual data wrangling.
This alignment doesn’t happen by accident. It requires initial planning, ongoing monitoring, and a willingness to refine processes as your organization learns what works. But the investment—measured in data quality improvement, time saved, and ultimately in customer relationships—delivers lasting value.



Liity yli 30 000 muun myynnin ja markkinoinnin ammattilaisen joukkoon. Tilaa Sell to Win -uutiskirjeemme!